Qu’est-ce qu’un investissement? Retour sur les principes de base.
Les performances du premier trimestre de 2013 ont été rien de moins que spectaculaires dans certains marchés. La bourse américaine a progressé de 11%, celle de la Suisse a avancé de 10%, le Nikkei japonais a monté de +9% tandis que certains petits marchés comme ceux de la Suède, du Mexique et de la Turquie ont bien performé. Au Canada, l’indice du SPTSX n’a pas été aussi reluisant. La faiblesse des secteurs des matériaux et des services publics a sérieusement plombé notre indice phare qui a terminé le premier quart de l’année en chute de 3%.
Cependant, depuis la fin de mars et le coup de départ du 2e trimestre, les marchés ont été affectés par un regain de volatilité. Bien que le marché américain se situe toujours au même niveau qu’à la fin du trimestre précédent, les titres canadiens chutaient de 6% alors que nous rédigions cette lettre en date du 17 avril 2013. Ce sont les ressources naturelles et l’or qui pèsent lourd dans l’équation.
L’Europe est toujours envenimée par la crise de l’endettement souverain qui empoisonne les pays périphériques de l’Union Européenne.
Pour ramasser les dégâts, les hautes instances européennes doivent répondre à ces deux odieuses questions : qui doit payer la note et comment doit-on la payer? En aparté, l’antidote nécessaire à la guérison de la plupart de ces maux est le temps. Il faut cependant s’attendre à des dislocations économiques, des défauts de paiement et des restructurations. Demeurez à l’écoute.
***************************************************
La fluctuation du prix de l’or, notamment sa violente chute des dernières semaines, questionne la pertinence d’investir dans l’or et dans les autres métaux précieux. Pour répondre à cette question, nous aimerions vous diriger vers un extrait de la lettre annuelle de Warren Buffet, adressée à ses actionnaires, en 2011. L’illustre investisseur partage sa pensée sur le sujet et explique avec doigté, pertinence et simplicité comment les investisseurs devraient analyser le sujet pour prendre une décision judicieuse. Comme nous ne sommes pas des traducteurs professionnels ici chez Claret, nous préférons vous présenter le texte dans sa version originale anglaise. Nous préférons que vos puissiez avoir accès à la couleur, à l’angle et aux images que nous partage l’auteur. Si vous n’êtes pas en mesure de bien comprendre son discours, nous vous invitons à communiquer avec nous.
The Basic Choices for Investors and the One We Strongly Prefer
Investing is often described as the process of laying out money now in the expectation of receiving more money in the future. At Berkshire we take a more demanding approach, defining investing as the transfer to others of purchasing power now with the reasoned expectation of receiving more purchasing power – after taxes have been paid on nominal gains – in the future. More succinctly, investing is forgoing consumption now in order to have the ability to consume more at a later date.
From our definition there flows an important corollary: The riskiness of an investment is not measured by beta (a Wall Street term encompassing volatility and often used in measuring risk) but rather by the probability – the reasoned probability – of that investment causing its owner a loss of purchasing-power over his contemplated holding period. Assets can fluctuate greatly in price and not be risky as long as they are reasonably certain to deliver increased purchasing power over their holding period. And as we will see, a non-fluctuating asset can be laden with risk.
Investment possibilities are both many and varied. There are three major categories, however, and it’s important to understand the characteristics of each. So let’s survey the field.
- Investments that are denominated in a given currency include money-market funds, bonds, mortgages, bank deposits, and other instruments. Most of these currency-based investments are thought of as “safe.” In truth they are among the most dangerous of assets. Their beta may be zero, but their risk is huge.
Over the past century these instruments have destroyed the purchasing power of investors in many countries, even as the holders continued to receive timely payments of interest and principal. This ugly result, moreover, will forever recur. Governments determine the ultimate value of money, and systemic forces will sometimes cause them to gravitate to policies that produce inflation. From time to time such policies spin out of control.
Even in the U.S., where the wish for a stable currency is strong, the dollar has fallen a staggering 86% in value since 1965, when I took over management of Berkshire. It takes no less than $7 today to buy what $1 did at that time. Consequently, a tax-free institution would have needed 4.3% interest annually from bond investments over that period to simply maintain its purchasing power. Its managers would have been kidding themselves if they thought of any portion of that interest as “income.”
For tax-paying investors like you and me, the picture has been far worse. During the same 47-year period, continuous rolling of U.S. Treasury bills produced 5.7% annually. That sounds satisfactory. But if an individual investor paid personal income taxes at a rate averaging 25%, this 5.7% return would have yielded nothing in the way of real income. This investor’s visible income tax would have stripped him of 1.4 points of the stated yield, and the invisible inflation tax would have devoured the remaining 4.3 points. It’s noteworthy that the implicit inflation “tax” was more than triple the explicit income tax that our investor probably thought of as his main burden. “In God We Trust” may be imprinted on our currency, but the hand that activates our government’s printing press has been all too human.
High interest rates, of course, can compensate purchasers for the inflation risk they face with currency-based investments – and indeed, rates in the early 1980s did that job nicely. Current rates, however, do not come close to offsetting the purchasing-power risk that investors assume. Right now bonds should come with a warning label.
Under today’s conditions, therefore, I do not like currency-based investments. Even so, Berkshire holds significant amounts of them, primarily of the short-term variety. At Berkshire the need for ample liquidity occupies center stage and will never be slighted, however inadequate rates may be. Accommodating this need, we primarily hold U.S. Treasury bills, the only investment that can be counted on for liquidity under the most chaotic of economic conditions. Our working level for liquidity is $20 billion; $10 billion is our absolute minimum.
Beyond the requirements that liquidity and regulators impose on us, we will purchase currency-related securities only if they offer the possibility of unusual gain – either because a particular credit is mispriced, as can occur in periodic junk-bond debacles, or because rates rise to a level that offers the possibility of realizing substantial capital gains on high-grade bonds when rates fall. Though we’ve exploited both opportunities in the past – and may do so again – we are now 180 degrees removed from such prospects. Today, a wry comment that Wall Streeter Shelby Cullom Davis made long ago seems apt: “Bonds promoted as offering risk-free returns are now priced to deliver return-free risk.”
- The second major category of investments involves assets that will never produce anything, but that are purchased in the buyer’s hope that someone else – who also knows that the assets will be forever unproductive – will pay more for them in the future. Tulips, of all things, briefly became a favorite of such buyers in the 17th century.
This type of investment requires an expanding pool of buyers, who, in turn, are enticed because they believe the buying pool will expand still further. Owners are not inspired by what the asset itself can produce – it will remain lifeless forever – but rather by the belief that others will desire it even more avidly in the future.
The major asset in this category is gold, currently a huge favorite of investors who fear almost all other assets, especially paper money (of whose value, as noted, they are right to be fearful). Gold, however, has two significant shortcomings, being neither of much use nor procreative. True, gold has some industrial and decorative utility, but the demand for these purposes is both limited and incapable of soaking up new production. Meanwhile, if you own one ounce of gold for an eternity, you will still own one ounce at its end.
What motivates most gold purchasers is their belief that the ranks of the fearful will grow. During the past decade that belief has proved correct. Beyond that, the rising price has on its own generated additional buying enthusiasm, attracting purchasers who see the rise as validating an investment thesis. As “bandwagon” investors join any party, they create their own truth – for a while.
Over the past 15 years, both Internet stocks and houses have demonstrated the extraordinary excesses that can be created by combining an initially sensible thesis with well-publicized rising prices. In these bubbles, an army of originally skeptical investors succumbed to the “proof” delivered by the market, and the pool of buyers – for a time – expanded sufficiently to keep the bandwagon rolling. But bubbles blown large enough inevitably pop. And then the old proverb is confirmed once again: “What the wise man does in the beginning, the fool does in the end.”
Today the world’s gold stock is about 170,000 metric tons. If all of this gold were melded together, it would form a cube of about 68 feet per side. (Picture it fitting comfortably within a baseball infield.) At $1,750 per ounce – gold’s price as I write this – its value would be $9.6 trillion. Call this cube pile A.
Let’s now create a pile B costing an equal amount. For that, we could buy all U.S. cropland (400 million acres with output of about $200 billion annually), plus 16 Exxon Mobils (the world’s most profitable company, one earning more than $40 billion annually). After these purchases, we would have about $1 trillion left over for walking-around money (no sense feeling strapped after this buying binge). Can you imagine an investor with $9.6 trillion selecting pile A over pile B?
Beyond the staggering valuation given the existing stock of gold, current prices make today’s annual production of gold command about $160 billion. Buyers – whether jewelry and industrial users, frightened individuals, or speculators – must continually absorb this additional supply to merely maintain an equilibrium at present prices.
A century from now the 400 million acres of farmland will have produced staggering amounts of corn, wheat, cotton, and other crops – and will continue to produce that valuable bounty, whatever the currency may be. Exxon Mobil will probably have delivered trillions of dollars in dividends to its owners and will also hold assets worth many more trillions (and, remember, you get 16 Exxons). The 170,000 tons of gold will be unchanged in size and still incapable of producing anything. You can fondle the cube, but it will not respond.
Admittedly, when people a century from now are fearful, it’s likely many will still rush to gold. I’m confident, however, that the $9.6 trillion current valuation of pile A will compound over the century at a rate far inferior to that achieved by pile B.
- Our first two categories enjoy maximum popularity at peaks of fear: Terror over economic collapse drives individuals to currency-based assets, most particularly U.S. obligations, and fear of currency collapse fosters movement to sterile assets such as gold. We heard “cash is king” in late 2008, just when cash should have been deployed rather than held. Similarly, we heard “cash is trash” in the early 1980s just when fixed-dollar investments were at their most attractive level in memory. On those occasions, investors who required a supportive crowd paid dearly for that comfort.
My own preference – and you knew this was coming – is our third category: investment in productive assets, whether businesses, farms, or real estate. Ideally, these assets should have the ability in inflationary times to deliver output that will retain its purchasing-power value while requiring a minimum of new capital investment. Farms, real estate, and many businesses such as Coca-Cola, IBM and our own See’s Candy meet that double-barreled test. Certain other companies – think of our regulated utilities, for example – fail it because inflation places heavy capital requirements on them. To earn more, their owners must invest more. Even so, these investments will remain superior to nonproductive or currency-based assets.
Whether the currency a century from now is based on gold, seashells, shark teeth, or a piece of paper (as today), people will be willing to exchange a couple of minutes of their daily labor for a Coca-Cola or some See’s peanut brittle. In the future the U.S. population will move more goods, consume more food, and require more living space than it does now. People will forever exchange what they produce for what others produce.
Our country’s businesses will continue to efficiently deliver goods and services wanted by our citizens. Metaphorically, these commercial “cows” will live for centuries and give ever greater quantities of “milk” to boot. Their value will be determined not by the medium of exchange but rather by their capacity to deliver milk. Proceeds from the sale of the milk will compound for the owners of the cows, just as they did during the 20th century when the Dow increased from 66 to 11,497 (and paid loads of dividends as well). Berkshire’s goal will be to increase its ownership of first-class businesses. Our first choice will be to own them in their entirety – but we will also be owners by way of holding sizable amounts of marketable stocks. I believe that over any extended period of time this category of investing will prove to be the runaway winner among the three we’ve examined. More important, it will be by far the safest.
********************************************
On nous questionne souvent dernièrement sur les perspectives futures des marchés boursiers. Bien que nous sommes heureux de partager avec vous nos pensées et nos opinions sur ce sujet, les prédictions macro-économiques ne représentent pas un critère décisif dans notre processus de sélection de titres d’équité. Cependant, même si nous considérons moins les prévisions économiques, nous demeurons néanmoins très à l’affût de l’état général des conditions financières.
-
Nos lecteurs assidus reconnaîtront certainement le graphique suivant qui a paru dans notre lettre du 3e trimestre de 2008. Voici une mise à jour de l’indice S&P 500 représenté en bleu par rapport à sa tendance à long terme en rouge. Ce graphique à long terme de l’indice phare des titres boursiers américains nous démontre qu’ils ont progressé sur une base de 6.1% composée annuellement au cours des 85 dernières années.
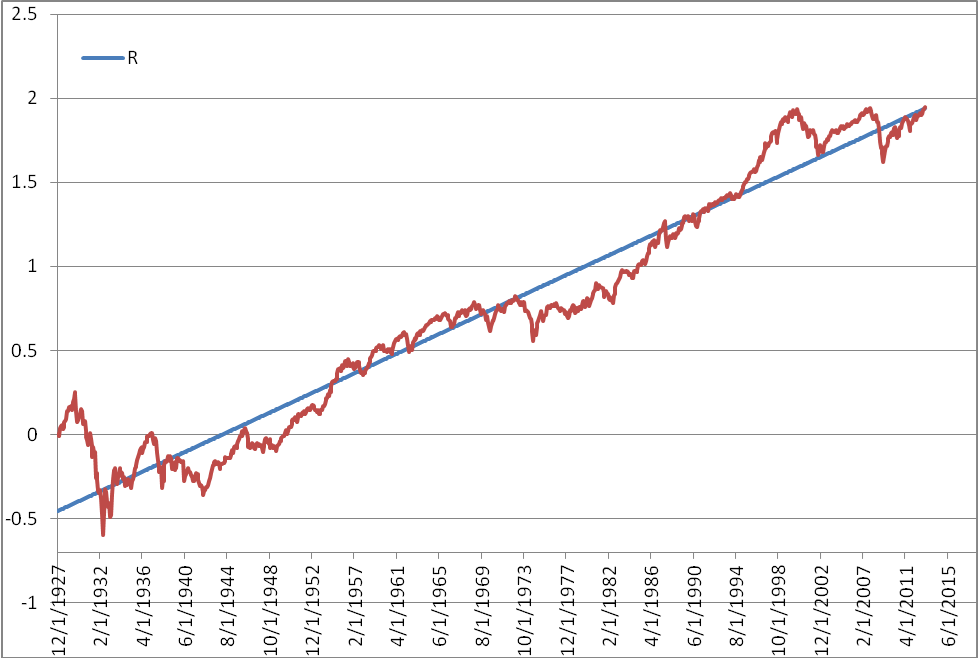
En simplifiant, la lecture de ce graphique nous démontre que les titres sont dispendieux lorsque le marché est au-dessus de sa tendance historique. Si le marché est dispendieux, alors la croissance à long terme devrait être sous sa moyenne historique. A contrario, lorsque les marchés naviguent sous leur tendance historique, comme ce fut le cas en 2008, les actions sont abordables et leur rendement devrait être au-dessus de leur tendance historique. Vous pouvez témoigner que le rendement de la portion actions de votre portefeuille, depuis le creux, a offert une performance significativement plus élevée que 6.1% !
Aujourd’hui, si on consulte ce graphique, nous pouvons conclure que le rendement des actions devrait être similaire à leur tendance à long terme. Nous convenons que cela est moins avantageux que si vous comptez à partir de la pointe inférieure de 2008, mais lorsqu’on compare ce rendement espéré à celui des obligations, il s’agit d’un scénario drôlement favorable.
-
Inflation ou déflation? Les économistes et prévisionnistes sont incertains de l’évolution future des prix à la consommation. Ils engagent de grands débats à ce sujet puisque l’enjeu de l’un envers l’autre est complètement différent. La logique conventionnelle nous porte à croire qu’il y aura de l’inflation puisque les gouvernements impriment de l’argent supplémentaire. Cependant, lorsqu’on se penche sur deux cas historiques qui partagent des similarités avec la crise financière de 2008, soit la continuité de la Grande Dépression de 1932 aux États-Unis et le cas japonais, les gouvernements y avaient imprimé une tonne de billets pendant plusieurs années sans conséquence inflationniste. Dans les faits, la déflation s’est quand même installée 3 ou 4 ans passé l’apogée de la crise.
Par ailleurs, même avec les presses à billets qui chauffent à travers le globe, l’inflation est contrôlée et faible malgré quelques soubresauts sporadiques. Peut-on imaginer quel aurait été le résultat si les banques centrales avaient limité la croissance de la masse monétaire? Est-ce que la déflation se serait installée pour de bon? En somme, l’emploi rarissime semble avoir freiné la croissance des salaires qui se veut une composante importante de l’inflation. En conclusion, tant que les entrepreneurs ne renouvellent pas leur confiance et leur optimisme quant aux perspectives économiques et quant à l’équité de la règlementation et des taxes, ils vont limiter la création d’emplois. Les entreprises devront créer beaucoup de nouveaux emplois pour éponger le surplus de travailleurs qui pollue l’économie.
-
L’évolution du dollar canadien importe aussi à nos interlocuteurs. Nous pensons donc valable de partager avec vous notre opinion sur l’évaluation de ce dernier. Nonobstant le niveau auquel il se transige, les investisseurs doivent se rappeler que le huard demeure une monnaie secondaire. Nous sommes donc à la merci des états d’âme des investisseurs étrangers. En d’autres mots, si les étrangers ont en tête que le Canada est un endroit prometteur pour l’investissement, notre dollar va monter plus qu’il ne le devrait. Par ailleurs, si les perspectives canadiennes devaient s’assombrir aux yeux des investisseurs, le dollar risquerait de s’affaiblir significativement plus qu’il ne devrait.
Depuis la crise financière de 2008, le Canada semble être le pays le mieux géré des pays développés. Ceci, combiné à une flambée des prix du pétrole et de l’or ainsi qu’à un système bancaire relativement robuste, a attiré beaucoup de capitaux chez nous. Tous ces facteurs appuyés les uns contre les autres ont ainsi contribué à faire augmenter la valeur du dollar canadien. Il se peut que les forces qui propulsent le huard aient passé leur paroxysme et qu’il manque des morceaux à la mosaïque qui soutient notre devise. Nous ne serions pas surpris de voir le dollar canadien retraiter au niveau des U.S. 90 sous. Qui plus est, si les prix du pétrole devaient poursuivre leur descente et que les dollars d’investissements étrangers devaient prendre la poudre d’escampette, le niveau des U.S. 80 sous n’est plus hors de question.
L’équipe Claret.






