Stock splits are all the rage lately. Google parent company Alphabet, Amazon, Tesla, and Shopify are among the latest companies to announce a stock split, and each has seen a post-announcement boost.
But what, exactly, is a stock split? And why are companies all of a sudden obsessed with splitting their shares? Here’s what you need to know about stock splits.
What are Stock Splits?
A stock split allows a company to break each existing share into multiple new shares, in theory, without affecting its market value or each investor’s stake in the company.
For example, a company might take one share of a stock and split it into two shares. The total combined value of the two new shares remains the same as the price of the previous single share.
Let’s say Company XYZ completed a 2-for-1 stock split. The original share price was $20 for one share.

The new two shares are each priced at $10. An investor who held fifty, twenty-dollar shares pre-split, would now own 100 shares at the new price of $10 each.

Although the number of shares outstanding increases by a specific multiple, the share price should drop in proportion to that multiple, because the split does not make the company more valuable.
Technically, a stock split has no fundamental impact beyond increasing the share count. However, correlation is not causation, and there are plenty of reasons to pay close attention to a company that announces split plans.
Why Do Companies Split Their Stocks?
A stock split is often a sign that a company is thriving and that its stock price has increased. While that’s a good thing, it also means the stock has become less affordable for investors. As a result, companies may do a stock split to make the stock more affordable and enticing.
As a company’s stock price increases, investors are rewarded with higher returns. Eventually, the stock may reach a price that makes it difficult for new investors to enter the market and purchase shares. This is where the stock split comes in.
Companies that split tend to do so because their stocks have risen significantly, and stocks with positive momentum often continue to increase.
Does a Stock Split Improve Returns?
Although the number of shares outstanding increases by a specific multiple, the share price should drop in proportion to that multiple, because the split does not make the company more valuable – or so the theory goes. In reality, it’s a bit more complicated.
In a September 2011 paper titled, The Information Content of Stock Splits, three esteemed professors determined that “stock splits contain more information about future, rather than past operating performance.”
If that’s true, stock splits could very well be a secret weapon for finding a successful company. If we look at S&P 500 companies that announced stock splits between 2012 and 2018, the results are staggering. Announcing a stock split typically results in an average immediate price boost of 2.5% for a stock. One year later, these stocks outperformed by an average of 5%.
Indeed, if we examine the table below, we can see that since 1980, S&P 500 stocks that announced stock splits have outperformed the index by an average of 16 percentage points the following year.
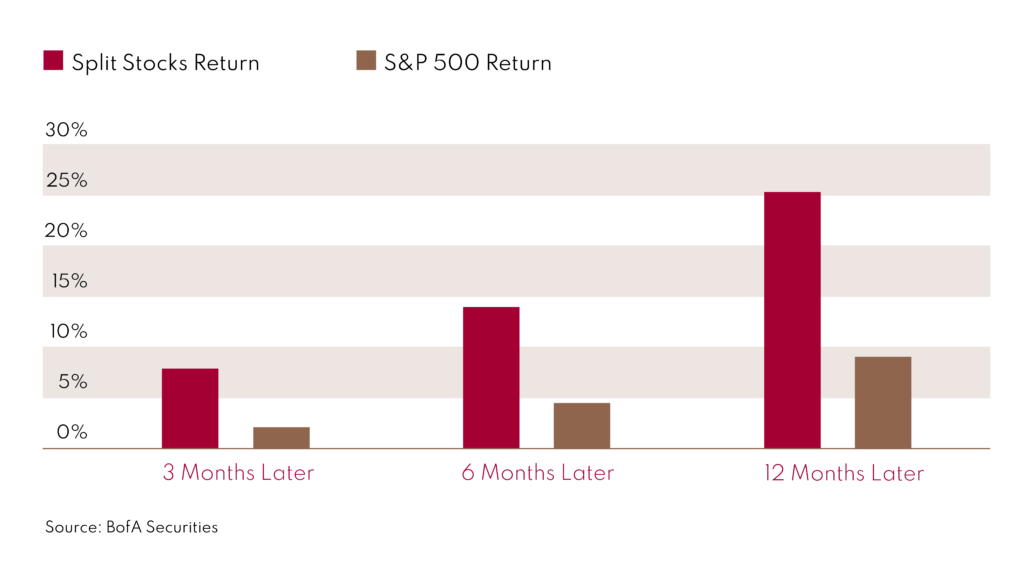
However, today’s market swings, caused in part by volatile earnings from previously high-flying tech companies and new expectations for the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet wind-down and rising interest rates, have led to a market decline. Many companies that have announced a split have seen their stock price returns dwindle since the announcement.
How Does a Stock Split Affect My Investments?
As a shareholder, you may be concerned that a stock split will impact your investment. Ultimately, there’s little impact on you as an investor. Investors will technically own more shares, but each share will represent a correspondingly smaller percentage of the company’s ownership.
“…stock splits contain more information about future, rather than past operating performance.”
The Information Content of Stock Splits.
Low share prices make it easier for retail investors to buy a small number of shares. Splits also had the effect of reducing stock trading commissions for smaller investors. However, the rise of commission-free trading platforms and fractional shares has made it easy for small investors to put as much cash as they want behind their favourite stocks.
Google (whose stock is now known as Alphabet), meanwhile, split its stock in 2014, giving shareholders a new, non-voting share for every share they already owned, and again underwent a conventional 20-for-1 split in July 2022. The 2014 split cemented the long-term control of the company’s founders — a controversial action that Facebook (now known as Meta) attempted to replicate with a new class of non-voting shares of its own, before abandoning the idea following protests from shareholders. Stock splits don’t change your voting power; votes scale in the same proportion as the split, so your percentage control stays the same. For example, if you held 100 Netflix shares (100 votes) before the split, you’d hold 1,000 shares (1,000 votes) after, but your percentage of total voting power stays precisely the same because everyone’s votes scale 10x.
If you’ve been considering investing in a particular company, a stock split signals that it’s doing well. Because the per-share price is lower, stock prices are also more affordable, allowing investors to potentially buy more shares.
Stock splits can certainly excite investors, but remember – they don’t directly affect the value of an underlying business. If you’re investing in a company after a stock split, approach it with the same level of analysis and curiosity that you would for any other company. It’s essential to conduct thorough research before making any investment. While a stock split can be a positive sign, other key metrics, such as revenue growth and market opportunity, are far more critical.







